Are you grappling with the complexities of second price auctions in the digital advertising space? Many advertisers face challenges in grasping this intricate bidding system. This guide simplifies second price auctions, providing clear explanations and effective strategies to elevate your advertising campaigns.
We at the Flying V Group have successfully executed programmatic ad campaigns for renowned companies such as Vasco Assets and Sauz Partners, yielding exceptional results. We’ll share the invaluable insights and experiences that have contributed to our success.
- What are Second Price Auctions?
- How does a Second Price Auction Work?
- What are the Advantages of Second Price Auctions?
- First Price Auctions vs Second Price Auctions: Which One Should You Choose?
- Unlocking Success with Flying V Group: Your Partner in Digital Growth
- FAQs
- What is a second price auction in Google Ads?
- How do you win a second price auction?
- How do you bid on a second price auction?
- What are the disadvantages of a second price auction?
- What is the difference between oral auctions and second-price auctions?
What are Second Price Auctions?
Second price auctions, also known as Vickrey auctions, are a unique auction format particularly popular in online advertising contexts. In these auctions, the highest bidder wins but only pays the amount of the second-highest bid.
How does a Second Price Auction Work?

Understanding how a second price auction operates is crucial for leveraging its strategic advantages, especially in online advertising. Let’s break down the process into steps and use an example of health supplement companies—NutriVital, HealthHarbor, VitaBoost, and GreenLeaf—bidding for an ad spot on a health blog.
Step 1: Placing Bids
In a second price auction, each bidder (in our example, the supplement companies) submits a single bid, typically in a sealed format, meaning no one knows the bid amounts of others. The bids reflect each company’s valuation of the ad space.
- NutriVital bids $100.
- HealthHarbor bids $150.
- VitaBoost bids $120.
- GreenLeaf bids $130.
Step 2: Determining the Winner
The auctioneer (or the advertising platform) then reviews these bids. The company with the highest bid wins the auction. In our scenario, HealthHarbor is the highest bidder with $150.
Step 3: Calculating the Payment
Unlike traditional auctions where the highest bidder pays their bid amount, in a second price auction, the winner pays the amount of the second-highest bid. Therefore, HealthHarbor pays $130, the bid placed by GreenLeaf, even though they bid $150.
What are the Advantages of Second Price Auctions?
Second price auctions offer several distinct advantages, particularly in the context of online advertising and bidding environments. These benefits not only make the auction process more efficient but also ensure fair pricing and strategic flexibility for all participants. Let’s explore some of these key advantages:
- True Value Bidding: One of the primary benefits of second price auctions is that they encourage bidders to bid their true value. Participants are incentivized to bid the maximum amount they’re willing to pay for the ad space or item, knowing they will most likely pay less if they win. This leads to more honest bidding and reduces the gamesmanship often seen in traditional auctions.
- Market Value Reflection: The winning bid in a second price auction typically reflects the item’s market value more accurately. Since the winner pays the second-highest bid, the final price is grounded in the valuation of multiple bidders, not just the winner’s possibly overestimated value.
- Reduced Winner’s Curse Risk: In standard auctions, there’s a risk known as the ‘winner’s curse‘, where the winner ends up overpaying. Second price auctions significantly reduce this risk as the winner pays a price closer to the market consensus rather than their potentially higher bid.
- Simplified Bidding Strategy: Bidders don’t need to engage in complex strategic planning or guesswork about other participants’ bids. They simply decide the highest amount they are willing to pay and bid accordingly, making the process more straightforward and less stressful.
First Price Auctions vs Second Price Auctions: Which One Should You Choose?
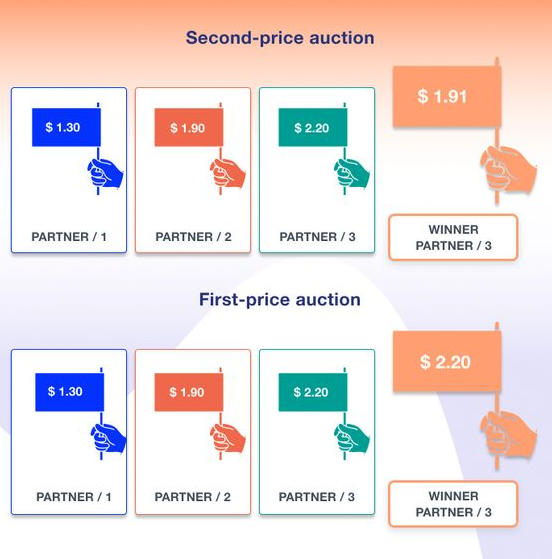
When it comes to selecting the right auction format for your advertising or selling needs, understanding the differences between first price auctions and second price auctions is essential. Both models have distinct advantages and considerations that can significantly impact your outcomes. Let’s compare the two to help you make an informed choice:
First Price Auctions:
- Winner Pays Their Bid: In a first price auction, the winner pays the exact amount they bid. This means that if you win with a high bid, you will pay that amount, potentially leading to overpayment.
- Strategic Complexity: First price auctions often involve more complex bidding strategies. Participants need to consider not only the value of the item but also the competitive landscape and how much others might bid.
- Winner’s Curse Risk: There’s a higher risk of the winner’s curse in first price auctions, where the winning bidder may end up overpaying if their bid significantly exceeds the competition.
Second Price Auctions:
- Winner Pays the Second-Highest Bid: In a second price auction, the winner pays the amount of the second-highest bid. This encourages true-value bidding, reducing the risk of overpayment.
- Honest Bidding: Participants in second price auctions are incentivized to bid their true value, simplifying the bidding process and reducing strategic complexity.
- Market-Driven Prices: The winning bid in a second price auction closely reflects the item’s market value, as it is based on the consensus of all participants.
Which One Should You Choose?
The choice between first price and second price auctions depends on your specific goals and the context of the auction. Here are some considerations:
- Budget Control: If you want more control over your budget and reduce the risk of overpayment, second price auctions are generally a safer choice.
- Simplicity: Second price auctions are simpler to participate in, making them suitable for situations where ease of use is a priority.
- Market Value: If you prefer the final price to closely reflect the market’s perception of value, second price auctions are ideal.
Unlocking Success with Flying V Group: Your Partner in Digital Growth
The journey to mastery in online advertising, particularly within the intriguing realm of second-price auctions, is a transformative experience.
It commences with a deep understanding of the intricacies involved and the deployment of effective bidding strategies. Second price auctions shine as a beacon of transparency, delivering unprecedented control and precision in assessing the actual value of ad spaces and items.
At Flying V Group, we transcend the role of mere digital marketers; we emerge as your dedicated partners in the quest for digital growth. Our team possesses a profound understanding of online advertising, including the nuanced world of second price auctions.
Regardless of whether you’re embarking on your advertising journey or seeking optimization, we stand ready with a rich arsenal of tools, knowledge, and experience to propel your campaigns to new heights. The journey towards advertising excellence awaits your exploration.
FAQs
What is a second price auction in Google Ads?
In a second price auction in Google Ads, the highest bidder wins but pays the amount of the second-highest bid. It encourages honest bidding and ensures that the winner pays a fair price, often resulting in better value for advertisers.
How do you win a second price auction?
To win a second price auction, place a bid that reflects the maximum amount you’re willing to pay for the item or ad space. The highest bidder wins, but they pay the amount of the second-highest bid.
How do you bid on a second price auction?
When bidding in a second price auction, determine the value of the item or ad space, and submit a bid equal to your maximum price. The highest bidder pays the amount of the second-highest bid.
What are the disadvantages of a second price auction?
Disadvantages of second price auctions include the potential for bidders to misjudge the value, strategic complexities, and the need to be aware of competitors’ bids.
What is the difference between oral auctions and second-price auctions?
Oral auctions involve public, verbal bidding, with the highest bidder winning and paying their bid amount. Second-price auctions, on the other hand, have sealed bids, and the winner pays the amount of the second-highest bid, promoting honest bidding.





0 Comments